Archive for September 2012
Step by Step ESXi 5 Installation and Configuration
Installation of ESXi 5.0 :
In this first Lab we will do a fresh interactive install of ESXi 5.0. This will involve mounting the ESXi 5.0 installation media into the Virtual Machine and then reset/reboot the virtual machine so that the VM will boot from the installation media.
The Virtual Machine that we will install ESXi 5.0 in is called ESXi 50 in the Lab Manager configuration that you deployed out to complete this Lab.
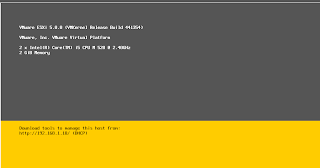
Here is what the VM should look at the moment.
So we can see that the VM has tried to boot, but no Operating System or installation media has been found.
The next step is to mount the ESXi 5.0 installation media and start the boot process. Mouse over the ESX50a tab at the top of the VM and a Menu will appear, select Insert CD… from this menu.
Go to VM setting and select esxi 5 iso imager from CD/DVD drive.
The media is called VMware-VMvisor-Installer-5.0.0-441354.x86_64.iso
The media should now be mounted, so Mouse over the ESXi 50 tab at the top of the VM and right click, select Reset from this menu.
Alternatively, you can press the CTRL – ALT – INS key sequence
The virtual machine will reset and it should boot from the installation media.
This is the first screen that you will be presented with. The Automatic timer will count down or you can press the Enter key to start the installation process.
You also have the option to press the Tab key to see the boot options.
Press enter and boot process will start….
Press Enter key to continue.
You will then be asked to Accept and Continue for the End User License Agreement (EULA).
Press the F11 function key to accept the EULA.
The installer will then scan the host for available Disks and you will be presented with a list of valid disks.
Note that the disks are separated out into Local: and Remote: storage devices.
Note that disks that have a VMFS Partition already on them will be displayed with an asterisk ( * ) next to them.
You also have the option to press the F1 function key to get additional details about the disks displayed.
This is what the detailed screen of the selected disk looks like.
Note the ESX(i) Found : No and Datastores: (none)
If you have pressed the F1 function key to get the detailed view of the selected disk, press the Enter Key now to return to the Select a Disk screen.
Press the Enter key to continue with the installation.
You will be asked to select a keyboard layout
Select your keyboard layout and press the Enter key ( we will use the Default )
Enter the password and press the Enter key to continue
You may see a screen come up with Error(s)/Warnings(s).
We can ignore these errors since we are running in a virtualized environment.
Press Enter to Continue
Press F11 to Install ESXi 5
The installation of ESXi 5.0 will being
If you press the ALT – F1 key sequence at this stage, you will see that you have a root login prompt.
You can login to the ESXi 5.0 host at this stage and have a look around at the logs if you want.
At this stage the ESXi 5.0 root password is blank.
If you press the ALT – F12 key sequence at this stage you will get to see the VMKernel logs.
The final entries ( ALT – F12) in the vmkernel logs will be as follows:
Pressing ALT – F2 key sequence will return you to the ESXi 5.0 Installer screen.
Once the installer has completed, you will see the following screen:
Do not Reboot the ESXi 5.0 host yet.
The next step is to un-mount the ESXi 5.0 Installation Media from the CDROM drive.
Mouse over the ESXi 50 tab at the top of the VM and right click Removable
device CD/DVD Disconnect.
You can now press the Enter key to Reboot the ESXi 5.0 Host.
The following message will appear :
The ESXi 5.0 host will now continue with the boot process and once completed, you will be presented with the following screen.
If DHCP is configured ESXi 5 will pick the IP address from DHCP server
The ALT – F11 screen should look like the following
Note from this screen, we can see some warnings: Warning: /vmfs/devices/char/vmkdriver/usbpassthrough not found
No need to be concerned about these for the moment, these are symptoms of running in a virtualized environment.
Move to the ALT – F2 screen
Press the F2 key to Customize System/View Logs
On the root login screen, enter root as the user and pass@123 as the password
This will bring you to the System Customization screen.
Note that the Configure Password is Set
The next step is to configure the ESXi 5.0 Networking and the DNS Settings.
Here are the settings that we will use to configure this host.
Select Set static IP address and network configuration ( use the arrow keys to move down and press the spacebar to select ) and change the IP Address, Subnet Mask and Default Gateway settings to the entries that we have outlined in the table above.
Once these values have been entered, press the Enter key.
We will next configure the DNS settings for this ESXi 5.0 host.
From the Configure Management Network menu, select DNS Configuration and press the Enter key
Here are the settings that we will use to configure this host.
ESXi 5.0 Configuration :
Now that we have the ESXi 5.0 host installed, we will continue and configure the Network SettingsMove to the ALT – F2 screen
Press the F2 key to Customize System/View Logs
On the root login screen, enter root as the user and pass@123 as the password
This will bring you to the System Customization screen.
Note that the Configure Password is Set
The next step is to configure the ESXi 5.0 Networking and the DNS Settings.
Here are the settings that we will use to configure this host.
IP Configuration :
|
Set static IP address and
network configuration
|
IP Addresss :
|
192.168.1.150
|
Subnet Mask :
|
255.255.255.0
|
Default Gateway :
|
192.168.1.253
|
From the System Customization menu, select Configure Management Network and press the Enter key
From the Configure Management Network menu, select IP Configuration and press the Enter keySelect Set static IP address and network configuration ( use the arrow keys to move down and press the spacebar to select ) and change the IP Address, Subnet Mask and Default Gateway settings to the entries that we have outlined in the table above.
Once these values have been entered, press the Enter key.
We will next configure the DNS settings for this ESXi 5.0 host.
From the Configure Management Network menu, select DNS Configuration and press the Enter key
Here are the settings that we will use to configure this host.
Primary DNS Server :
|
192.168.1.99
|
Secondary DNS Server:
|
(blank)
|
Hostname :
|
ESXi50.redback.com
|
Press the Enter key on the DNS Configuration menu. Enter the details as outlined in the above table
Once these settings have been entered, press the Enter Key.The DNS Configuration screen should change to the following:
Press the ESC key to return to the Customize System menu.
Since we changed the host management network, you will have to confirm that you want to Apply changes and restart management network.
Press Y key to accept the changes.
Press the ESC key once more to return to the Main ESXi 5.0 console screen.
New in vSphere 5.0 Networking
In vSphere 5.0 vmware comes up with
two new Networking Capabilities in virtual Distributed Switch.The first
improves the network administrator’s ability to monitor and troubleshoot
virtual infrastructure traffic by introducing features such as
·
NetFlow
·
Port mirror
The type focuses on enhancements to
the network I/O control (N I OC) capability first released in vSphere
4.1. The enhancements to NIOC enable customers to provide end-to-end
quality of service (QoS) through allocating 1/0 shares for user-defined traffic
types as well as tagging packets for prioritization by external
network infrastructure.
·
User-defined resource pool
·
vSphere replication traffic
type
·
IEEE 802lp tagging
Network Monitoring and
Troubleshooting
Network administrators
require more control on the traffic flowing between virtual infrastructure
& from virtual infrastructure to physical infrastructure. The new
functionality in vSphere 5.0 Distributed Switch to monitor
& troubleshoot networking issues provides more visibility on the traffic.
Net Flow :
NetFlow
v5 is a networking protocol is most common version and is supported by most of
the network devices. NetFlow collects IP traffic information and sends them to
a collector for flow analysis. With NetFlow capability on a vDS with NetFlow
collector tool helps in application monitoring and capacity planning. This also
help administrator to ensure that I/O resources are utilized properly by
different applications as per there needs. NetFlow on vDS can be enabled
at
·
Port Group Level
·
Individual Port Level
·
Uplink Level
Port Mirror :
The Port
Mirroring configured on vDS provides ability to network administrator in
debugging network issues in a Virtual Infrastructure. Port Mirroring in vSphere can also be referred to as
Switch Port Analyzer on Cisco Switches. Port Mirroring sens a copy of network
packets seen on a switch port to a network monitoring device connected to
another switch port. Once Port Mirroring is configured with a destination vDS
copies packets to the destination (the traffic destination can be any VM,
vmknic or uplink port).
Network Management and
Configuration :
These days different vendors comes
up with different type of Virtual & Physical networking devices and the
data center environment is getting complex to manage and configure because
of heterogeneous networking devices from different vendors.
vSphere 5.0 comes up with supports
for IEEE 802.1AB Standard – based Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) for
management & configuration of heterogeneous networking devices in data
center.
LLDP ( Link Layer Discovery Protocol
) :
LLDP is a vendor-neutral Link Layer
protocol in the Internet Protocol Suite used by network devices for advertising
their identity, capabilities, and neighbors on a IEEE 802 local area network
LLDP performs functions similar to
several proprietary protocols, such as Cisco Discovery Protocol, Extreme
Discovery Protocol from Extreme Networks, Nortel Discovery Protocol (also known
as SONMP), and Microsoft’s Link Layer Topology Discovery (LLTD).
Virtual infrastructure administrator
can enable this feature on vDS by selecting LLDP discovery protocol with
following options
·
Listen
·
Advertise
·
Both
Network Traffic Management
As more and more
critical applications are being run virtualized environment its
become important to manage the traffic flowing though a physical network
interface to avoid Low – Priority traffic consuming all the network resources.
In VMware vSphere 5, NIOC (Network
Input / Output Control) supports traffic management for following type of
traffics
·
Management traffic
·
iSCSI traffic
·
Virtual Machine traffic
·
NFS traffci
·
Fault Tolerant traffic
·
VMware vMotion traffic
·
User – defined traffic
·
vSphere replication traffic
Through NIOC a network administrator
can allocate I/O shares and limits to different type of traffic types.
Administrators can now create user defined traffic types and allocate
shares and limits to them.
vSphere Replication Traffic is a new system traffic. vSphere replication traffic
once configured on vDS under resource allocation with configured shares &
Limits parameter helps to provide required network resources to the
replication process.
User – Defined Network Resource Pools
User defined network resource pools
provide an ability to add new traffic types that are used for I/O Scheduling.
User Defined Network resource pools can be defined at vDS level. Once a new
network resource pool is defined with shares and limits, the resource pool can
be associated with a port group. Associating Network resource pool to a port
group enables to allocate I/O resources to a group of virtual machines or
workloads.
IEEE 8.02.1P Tagging
Tagging network packets with IEEE
802.1P BIT for prioritization provide capability to guarantee I/O resources to
the traffic generated from business critical applications & helps in
providing QoS to the business critical applications. IEEE 802.1P is a
3BIT field which differentiate packets into seven different traffic
classes.
It is not sufficient to provide I/O
resources just at host level for a business critical application unless it is
not planned to provide end – to – end QoS. Once configured on vDS switch
network administrator can edid the QoS priority tag field by choosing any
number from 1 – 7
Tag :
vSphere 5.0